Imagine trying to buy tickets for your favorite band’s concert, only to find the website down just minutes before they sell out. Or logging into the cloud to look through your cherished digital photos and discovering they’ve been lost because of a data center failure.
These scenarios are — at best — frustrating for you. But, for your customers, they can erode trust and damage your business’s reputation.
That’s why organizations invest in strategies like high availability (HA) and fault tolerance (FT). Both aim to keep systems operational with minimal-to-zero downtime. Yet each takes a different approach to reliability. In this article, we’ll explore the defining characteristics, practical use cases, and trade-offs of HA and FT to help you choose the right path for your company’s requirements.

What is High Availability?
In technology, "availability" refers to the amount of time a system is accessible to users or interconnected services. If a system is offline, it can’t fulfill its purpose — much like a vending machine that’s always out of your favorite snack. Availability is typically quantified as a percentage of uptime over a year. For example, 99.99% uptime (“four nines”) translates to just 52.6 minutes of downtime per year. Many companies, such as service providers, formalize their promised availability for their customers through service level agreements (SLAs). This ensures that downtime is an exception rather than the norm.
High availability describes an architectural strategy geared toward keeping systems operational as much as possible. Typically, an HA system aims for 99.999% uptime or better, minimizing both the instances and duration of downtime. With high availability architectures, service interruptions tend to be brief — if they happen at all.
Even if you’re not delivering services to external clients, many businesses rely on high availability to support internal processes. For instance, organizations running e-commerce platforms or financial applications prioritize HA to ensure transactions and payments never stall due to outages.
What is Fault Tolerance?
Where high availability focuses on keeping downtime to a minimum, fault tolerance strives for zero downtime. Although both share the goal of continuous service, fault tolerance requires deeper redundancies and more advanced mechanisms to instantly handle any failure.
Due to the complexity and cost, fault tolerance isn’t essential for every system. If a brief outage is acceptable (for example, a few seconds of downtime during a low-traffic period for e-commerce), high availability may suffice. However, for critical services — like air traffic control — no interruption is acceptable. This makes fault-tolerant design mandatory to guarantee continuous operation in every circumstance.
How do they work?
High-availability solutions typically use strategies like failover, load balancing, and redundant infrastructure to keep downtime to an absolute minimum. Fault-tolerant systems then take these same HA techniques to the next level by adding extra redundancies, aiming to eliminate service interruptions — even if one or more components fail.
| High Availability | Fault Tolerance |
|---|---|
|
|
Monitoring and alerting solutions are also critical for both high availability and fault tolerance, as they detect operational issues in real time and immediately alert technical teams before service is disrupted. These tools continuously track the health of IT infrastructure, scanning for everything from disk space usage to CPU and network performance, and triggering alerts the moment anomalies arise.
For instance, Nagios and Zabbix are widely used to keep tabs on system health, disk capacity, network activity, and CPU usage. Meanwhile, AWS CloudWatch and Azure Monitor deliver real-time insights into cloud resources, promptly notifying administrators of any irregularities.
AI-driven predictive analytics and maintenance solutions often come to mind when discussing critical industries and operations. By anticipating failures before they occur, these systems significantly reduce downtime. For example, airlines rely on predictive maintenance to monitor aircraft engine performance, helping them avoid unexpected breakdowns and minimize flight delays. This level of proactive oversight also exemplifies fault-tolerant design, ensuring continuous operation even when components start to fail.
High Availability vs. Fault Tolerance
When considering whether your systems should be designed for high availability, fault tolerance, or a mix of both, it’s a good idea to weigh up cost, performance, and complexity.
-
Cost and complexity. Fault-tolerant architectures are more expensive to develop and maintain because each component requires multiple redundant copies. This can amplify expenses related to hardware, software, and staffing. For many organizations, a highly available system strikes the right balance of uptime and cost-effectiveness.
-
Performance and scalability. High-availability clusters can improve performance under normal conditions by distributing the workload, whereas fault-tolerant backups typically remain idle until needed. Adding load-balancing to fault-tolerant setups further increases costs and complexity.
-
Data overheads and latency. Both HA and FT rely on real-time data replication, which may introduce additional overhead. In latency-sensitive scenarios, these overheads should be carefully managed.
-
Recovery Time Objective (RTO). Fault-tolerant systems aim for an RTO of zero. So they must fail over immediately, with no data loss. High availability can tolerate minimal interruption, using backups or snapshots to get back online quickly if needed.
Fault Tolerance & High Availability best practices
-
Complete redundancy. Ensure there’s no single point of failure. This includes everything from servers and databases to network equipment.
-
Automated detection and response. Implement monitoring tools to instantly flag issues and trigger failover or self-healing actions, notifying engineering teams simultaneously.
-
Geographical resiliency. For additional fault tolerance, deploy fully replicated systems in separate regions. Even for high availability, having a mirrored data store off-site can expedite recovery.
-
Robust backups. Regardless of your chosen availability strategy, reliable backups remain non-negotiable. They protect against accidental deletions, major disasters, and other unpredictable events. It’s also a typical compliance requirement.
-
Watch the costs. Redundant systems can quickly become expensive. Carefully assess both initial investments and ongoing upkeep to maintain control of your budgets.
High Availability & Telemetry Pipelines
When it comes to managing telemetry data or even just logs — whether they’re application logs, system logs, or security logs — high availability is critical for maintaining visibility and control across your IT environment. After all, trying to troubleshoot without logs is like trying to find a needle in a haystack. Chances are, you never will.
Let’s delve into the main reasons why telemetry pipelines and log management systems must be equipped with high-availability and fault-tolerance features:
-
Continuous Insight. If your log management platform goes down, you lose real-time insight into system performance and security events. This can be particularly dangerous when investigating incidents or outages elsewhere in the infrastructure.
-
Prompt Issue Detection. Monitoring tools and automated alerts often rely on log data to trigger notifications about anomalies (e.g., spikes in error rates, unauthorized access attempts, etc.). A highly available log management system ensures these alerts are neither delayed nor lost, allowing teams to respond before small issues become major incidents.
-
Compliance and Auditing. Many industry regulations (like HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR) demand comprehensive and continuous logging to demonstrate compliance. Missing or incomplete logs due to downtime can compromise audit trails and potentially result in fines or penalties.
-
Forensic Analysis. In the event of a security breach or outage, historical logs are invaluable for root-cause analysis and forensics. A highly available log management system is more likely to capture and retain the necessary records without gaps that might obscure the timeline of events.
-
Scalability and Performance. High availability strategies, such as clustering and load balancing, help log management systems efficiently handle significant volumes of data. As log data grows, these architectures enable your logging solution to scale without introducing single points of failure.
-
Business Continuity. Logs are often used to track user activities, system behaviors, and transactional data. Interruptions in log collection or analysis could hamper troubleshooting and undermine confidence in the overall reliability of your services.
By ensuring the high availability of your telemetry pipeline or log management solution, you safeguard the continuous flow of crucial operational and security data. Furthermore, you remain proactive in detecting and reacting to potential threats and performance issues. This level of resilience instils trust in your digital infrastructure and supports the smooth operation of every system that relies on real-time and historical log data.
What about NXLog?
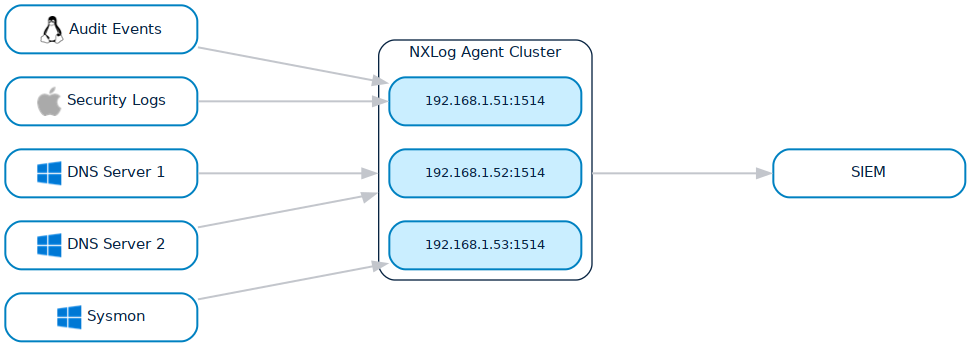
NXLog Platform provides high availability by supporting both failover and load balancing of data collectors/relays, ensuring continuous, reliable log collection. In a failover (active-passive) scenario, NXLog automatically reroutes logs to a backup collector node if the primary node fails. Load balancing, meanwhile, relies on an active-active architecture to distribute workloads across multiple collector nodes, improving performance and preventing any single system from becoming a bottleneck.
Furthermore, NXLog Agent buffers data at the edge if the destination (receiver) is temporarily unavailable, then automatically resends it once the destination is ready, ensuring no data is lost. Combination of these capabilities help organizations maintain both resilience and efficient performance in their log collection infrastructure.
Check our documentation to learn more: High Availability (HA) | NXLog Platform Documentation
